

Effect of concentration of NaCl in electrolyte on the product of electrolysisĬase 1) When the concentration of NaCl is low (highly diluted solution): At a higher dilution of NaCl, water dominates the electrolyte. ii) At anode, the product will be chlorine gas or oxygen gas.Ī side product of NaOH is also formed depending on the concentration of NaCl in water.i) At cathode, the product will be sodium metal or hydrogen gas.Hence, the major product formed from the electrolysis of aqueous NaCl. This process is also known as the Chlor-Alkali process because the products constituted are chlorine (chlor) and NaOH (alkali).Also, the Na+ ion and OH- ion in the remaining solution react together to form NaOH Hence, the end product of the electrolysis of NaCl produces H2 gas at cathode and Cl2 gas at anode.Also, in the case of an aqueous solution, water also gets dissociated into H+ ion, and OH- ions, and they also participate in the electrolysis reaction.Generally, the electrolysis of NaCl, when dissolved in water, becomes a lot easier than the electrolysis of NaCl in the molten state.Sodium Chloride is an ionic salt that readily dissociates in water as sodium cation and chloride anion.This usually depends on the reduction potential of ions, which is highly affected by the voltage of the current supplied. Sometimes kinetically stable products are formed due to this. Generally, electrolysis reactions prefer thermodynamically stable products, but if there is an oversupply of voltage during the reaction, it alters the end product. Not only that, in the aqueous phase of the salt, water also participates in the electrolysis and alters the end product. The reduction of potential variation of ions leads to the generation of multiple ionic products sometimes. The ions in the electrolyte have a major influence over the end product formed. If the concentration of salt or acid or base in the electrolytic solution is altered, then it also brings change to the major product formed in the reaction.
ANODE AND CATHODE IN ELECTROLYSIS FREE
Hence, the electrolyte must contain free mobile ions in order to complete the process of electrolysis. In general, electrolysis involves the movement of charged particles such as ions (cations and anions) towards the oppositely charged electrodes. Hence, if the electrolyte is non-conducting or contains no ions, then it will stop the process of electrolysis. Generally, current needs a carrier such as electrons to flow through a material. But if some non-reactive or inert electrodes such as that of platinum or graphite are used, then they possess no change in them.įor example: In the electrolysis of a solution of sulfuric acid in water, if platinum electrodes are used, then there will be no reduction by platinum at anode, and the concentration of sulphate ion starts increasing in the solution, but if electrodes of copper are used at anode then it will reduce the sulphate ion to maintain its concentration.

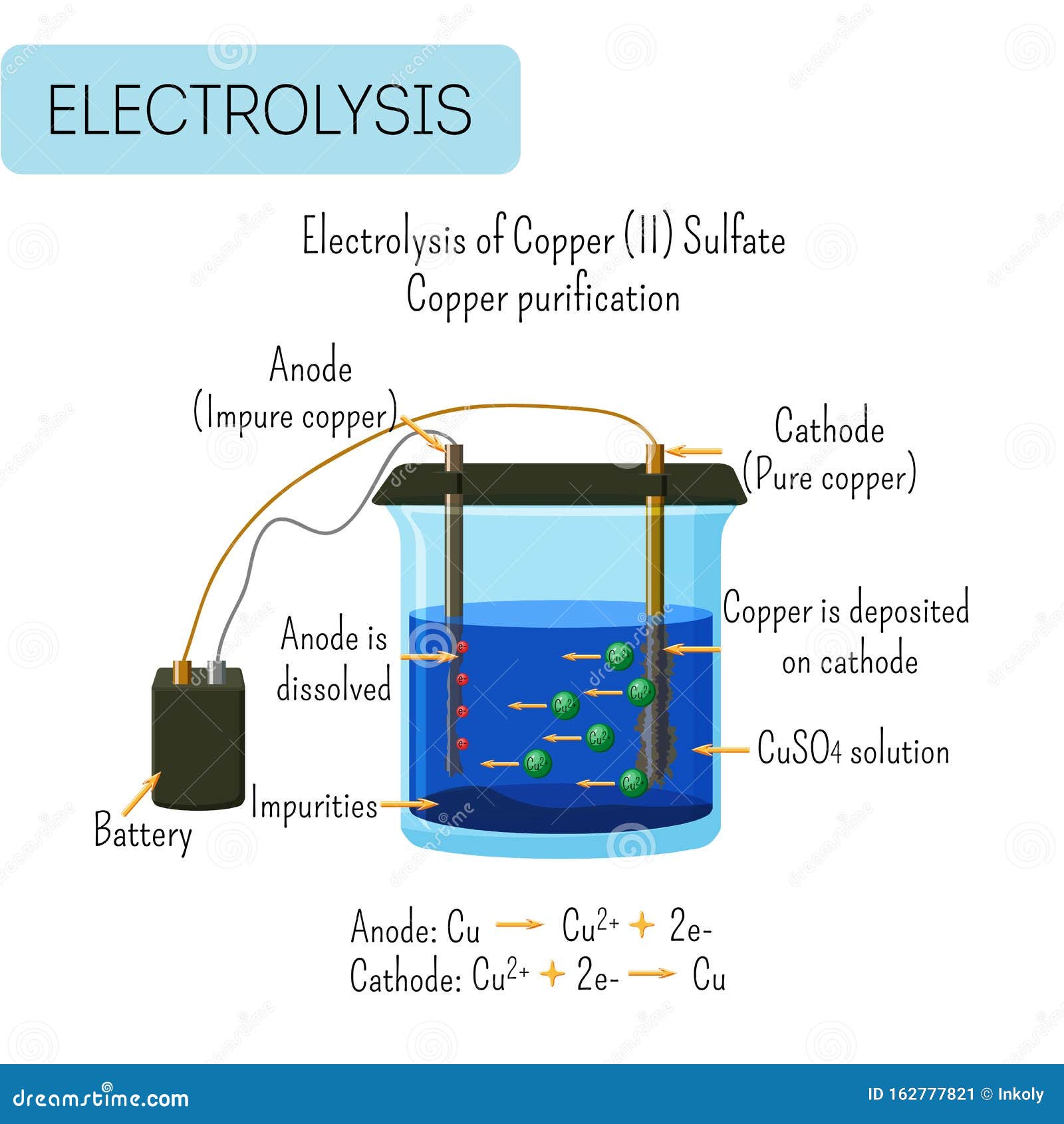
If the electrode contains metals that are more reactive or have a high reduction tendency, then it will readily react with the ions of the electrolyte and start decreasing in size.
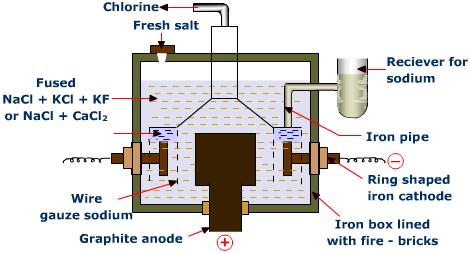
The extent of electrolysis depends majorly on the electrodes dipped in the electrolytic solution. There are various factors that affect the electrolysis of a compound.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
